
colidescope
/guides/ 04-intro-to-python-01-getting-started-with-python
colidescope
/guides/ 04-intro-to-python-01-getting-started-with-pythonIntro to Python
This guide will introduce the programming language Python and demonstrate how it can be used within Grasshopper to access Rhino's core geometric functions.
Getting started with Python
In this tutorial you will learn how to access the Python programming language from within the Grasshopper environment by using the special Python component. By the end of the lesson you will be ready to start writing Python code in the next exercise.
¶Other sections in this guide
| Intro to Python | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Getting started with Python |
| 2 | Exercise: Working with the Rhino API |
| 3 | Working with data in Python |
¶Python in Rhino and Grasshopper
Starting in version 5, Rhino has Python directly embedded alongside (and as an eventual replacement for) Rhinoscript. In addition to running any standard Python code, it can also import the Rhino API which allows you to work with Rhino's native Classes including all of it's geometry types. Using these libraries designers can use Python to control almost every feature of Rhino, from the model geometry, to its views, cameras, and even the user interface.
You can also work with Python directly in Grasshopper through a special Python component. In the past you needed to download an external Grasshopper library to get access to this component but the Grasshopper included in the latest versions of Rhino (6 and 7) come with this component installed. This means there is nothing extra to install and as long as you have Rhino 6 or 7 you have everything you need to start working with Python in Grasshopper!
The great thing about working with Python in Grasshopper is that it allows you to mix and match between working with code and normal Grasshopper components. This way, there is no pressure to develop your entire model just through code starting with a blank text file, which can be very intimidating for those just starting out with scripting or computational design.
Instead, you can develop most of the model using standard Grasshopper components, and only use Python code to do more complex tasks that are difficult or impossible in standard Grasshopper. In this way, the Python component provides a great gateway into the possibilities of using code for computational design. You can start off by writing small, simple scripts for specific purposes, and gradually develop more and more complex code as you learn.
¶Using the Python component
To get started with Python in Grasshopper, you can find the Python component in the Maths tab of Grasshopper.
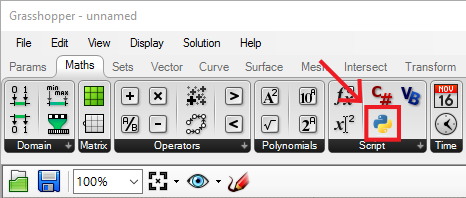
Let’s put one of these components onto the canvas and see how it works. You can see that the Python component has input and output ports just like any other component in Grasshopper, except it can have any number of inputs and outputs and you can call them whatever you want.
You can add more inputs and outputs by zooming in on the component until you see minus icons appear next to the input/output names and plus icons appear between them. You can use these icons to either add or remove inputs and outputs. You can also rename them by right clicking on the name and entering a new name in the text box at the top of the menu.
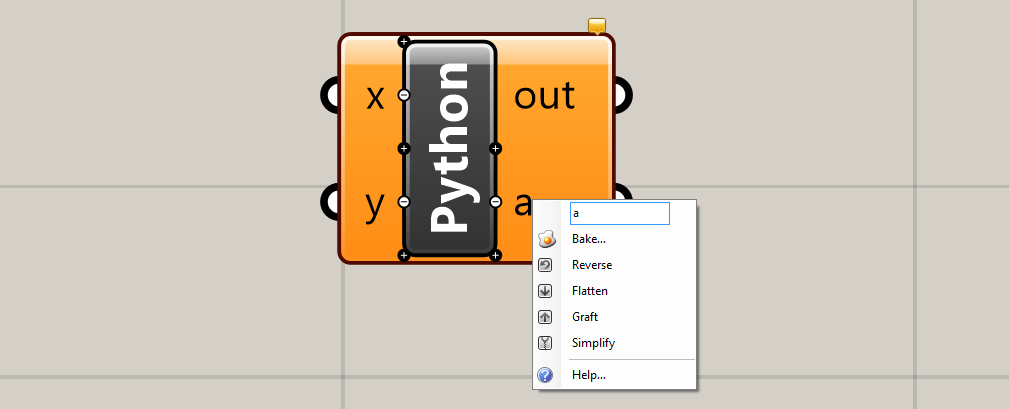
These inputs and outputs are automatically brought into the Python script where you can use them as variables. This allows the Python script to interact with the rest of your Grasshopper model by bringing data in through input variables and then outputting other data that was created within the script.
Double clicking on the center of the component brings up the script editing window where you can write the actual Python code. Let’s create a simple ‘hello world’ example to see how this works.
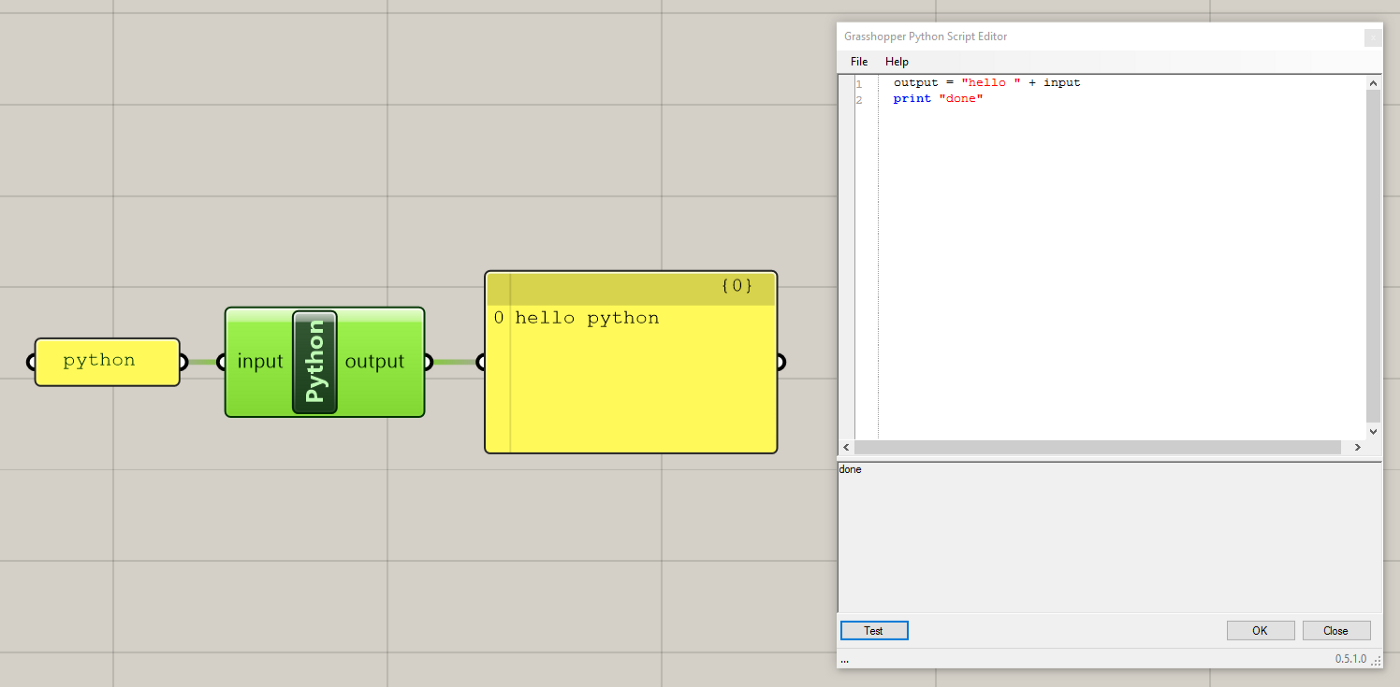
GHPython ‘hello world’
Change the name of one of the Python component's inputs to ‘input’ and the name of one of the outputs to ‘output’. Connect a Panel component into the input and type whatever you want into the Panel. Attach another Panel component to the output so we can see the results.
Now type this line of code into the script window:
output = "hello " + input
and click the Test button at the lower left corner of the code window. This button will execute the script and you should see the results above. Clicking OK will save changes to your script and close the editor window. Clicking Close will close the window without saving changes. This simple example brings in text from the Grasshopper canvas through its input port, joins this text to another piece of text, and then assigns the result to the output port, which can then be used on the Grasshopper canvas.
Conclusion
We now have a solid foundation for how to run Python code from within the Grasshopper environment. Integrating code into Grasshopper like this is a very powerful way to extend the basic functionalities of Grasshopper and will allow us to create interesting and complex models using the full tools of computation. You should think of the Python component as a way to create your own custom components in Grasshopper. In fact, each Grasshopper component does contain code that tells it what to do, except the code is hidden from us and written in a different programming language.
At this point you should be ready to start learning Python. You can now go on to the next exercise where we will learn how to import the Rhino libraries into Python which will give us access to all of Rhino's native classes, including it's geometry types, so we can start working with them within our Python scripts.
The final guide of the series will introduce basic concepts for how data is represented and manipulated in Python which are not specific to geometry or Rhino and can be run in any environment. However, unless you have a reason to run Python elsewhere I would encourage you to follow along with those tutorials by typing the code and executing it within a Python component in Grasshopper. Although it can be tempting to just read through the code samples, the best way to learn and retain knowledge is by writing out the actual code yourself (avoid copy/paste if you can!) and stumbling on and fixing bugs in syntax as you go.
¶Learning more
For more information about learning the Python programming language you can follow these guides:
- https://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide/NonProgrammers
- https://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide/Programmers
For more specific information on working with Python in Rhino and Grasshopper you can consult these resources:
- http://developer.rhino3d.com/guides/rhinopython/ — Rhino’s Python support page.
- http://www.rhino3d.com/download/IronPython/5.0/RhinoPython101 — book about using Python in Rhino.
- https://developer.rhino3d.com/api/RhinoCommon/html/R_Project_RhinoCommon.htm — documentation of the Rhino API. This includes documentation of all of Rhino's native Classes as well as code samples in Python as well as C# and VB.
- http://developer.rhino3d.com/api/RhinoScriptSyntax/win/ — documentation of the rhinoscriptsyntax library. This is a helper library that makes some functionalities easier to write in code. It was developed to replicate some of the functionalities of the old RhinoScript syntax making it easier to transition from RhinoScript to Python.
- http://developer.rhino3d.com/guides/rhinopython/python-rhinoscriptsyntax-introduction/ — support for the rhinoscriptsyntax Python library.